Table of Contents
- What is RCS?
- The Journey of RCS on Android
- RCS on iPhones: A New Era!
- ProTexting and the Role of RCS Providers
- The Benefits of RCS for Businesses
- The Future of RCS and Messaging
- Additional Sections for Comprehensive Coverage
- Historical Context of SMS and the Evolution of RCS
- The Birth of RCS
- Comparison of RCS with Other Messaging Protocols
- Case Studies of Businesses Using RCS
- Challenges and Limitations of RCS
- User Guides and Best Practices for RCS
- Future Outlook and Predictions
Text messaging has come a long way since the first SMS was sent in 1992. While traditional SMS (Short Message Service) has served us well, the evolution of mobile communication has demanded more. Enter Rich Communication Services (RCS), a protocol designed to enhance and modernize text messaging. RCS offers features akin to popular messaging apps, making communication more interactive and engaging.
This blog post explores RCS’s intricacies, its significance in the mobile communication landscape, and the recent introduction of the iPhone. We’ll also explore how providers like YepText leverage RCS to offer innovative solutions for individual users and businesses.

What is RCS?
Rich Communication Services (RCS) is a communication protocol that replaces SMS and MMS messaging. It was developed by the GSM Association (GSMA) to provide a more enriched messaging experience. RCS allows more dynamic interactions than SMS, and it is limited to 160 characters per message.
Key Features of RCS:
- Rich Media Sharing: Unlike traditional SMS, RCS supports the transmission of high-resolution photos, videos, and audio messages without the limitations of file size and quality.
- Typing Indicators: With RCS, you can see when someone is typing a response, similar to features found in apps like WhatsApp and Messenger.
- Read Receipts: Know when your message has been read, providing more transparency and improving communication efficiency.
- Group Chats: RCS supports advanced group chat functionalities, including adding or removing participants and seamlessly sending messages to all group members.
- Location Sharing: Easily share your real-time location with others.
- Improved Security: RCS provides better security features than SMS, including end-to-end encryption in some cases.
The Journey of RCS on Android
RCS has been available on Android devices for several years. Google has played a pivotal role in its adoption and implementation, integrating it into its Android Messages app. Given the open nature of the Android platform and Google’s significant influence, the transition to RCS on Android was relatively smooth.
Implementation and Adoption:
- Google’s Role: Google has been a major proponent of RCS, incorporating it into its Android Messages app and pushing for carrier support globally. This has facilitated the widespread adoption of RCS among Android users.
- Carrier Support: For RCS to work, carriers must support the protocol. Major carriers worldwide have gradually adopted RCS, recognizing its potential to enhance user experience and compete with over-the-top (OTT) messaging apps like WhatsApp and iMessage.
- Universal Profile: The GSMA developed the Universal Profile for RCS to ensure compatibility and a seamless experience across different devices and networks. This set of standards ensures that RCS works consistently, regardless of the carrier or device manufacturer.
RCS on iPhones: A New Era!
The introduction of RCS on iPhones is a significant milestone in the messaging landscape. For years, iPhone users were limited to SMS or Apple’s proprietary iMessage for enhanced features. The recent rollout of RCS on iPhones marks a new era in mobile communication, offering a unified messaging experience across both major mobile platforms.
Why This is a Big Deal:
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: With RCS, Android and iPhone users can now enjoy a seamless messaging experience. This eliminates the fragmentation that has long existed between the two platforms.
- Enhanced User Experience: iPhone users can now access features like high-quality media sharing, typing indicators, and receipt reading that were previously unavailable through traditional SMS.
- Business Communication: RCS opens up new opportunities for businesses to engage with iPhone users more effectively and meaningfully.
How to Enable RCS on iPhones:
- Software Update: Ensure your iPhone is running the latest iOS version. RCS support is typically included in recent software updates.
- Carrier Settings: Depending on your carrier, you may need to enable RCS through your device’s carrier or messaging app settings.
- Messaging App: Some carriers may require you to use a specific messaging app that supports RCS. Ensure you have the appropriate app installed and configured.
ProTexting and the Role of RCS Providers
ProTexting is a leading provider of RCS messaging services, offering robust solutions for businesses looking to leverage this advanced messaging protocol. Their platform enables businesses to create more engaging and interactive communication strategies, enhancing customer engagement and satisfaction.

How ProTexting Utilizes RCS:
- Marketing Campaigns: ProTexting enables businesses to send rich media marketing messages, including images, videos, and interactive content, directly to customers’ messaging apps.
- Customer Support: Businesses can use RCS for real-time customer support, which provides a more efficient and satisfying experience than traditional SMS.
- Transactional Messages: Send important transactional messages, such as order confirmations and delivery updates, with enhanced features like read receipts and interactive buttons.
- Surveys and Feedback: Collect customer feedback and conduct surveys through interactive RCS messages, making it easier for customers to respond.
The Benefits of RCS for Businesses
RCS offers numerous benefits for businesses, transforming how they communicate with customers. Here are some key advantages:
1. Enhanced Customer Engagement:
- Rich Media: Businesses can send high-quality images, videos, and audio messages, creating a more engaging and immersive experience for customers.
- Interactive Features: RCS supports interactive buttons, allowing customers to act directly within the message, such as making a purchase, booking an appointment, or providing feedback.
2. Improved Customer Support:
- Real-Time Communication: Features like typing indicators and read receipts allow customer support representatives to provide more timely and effective assistance.
- Multimedia Support: Customers can send photos or videos to illustrate issues, making it easier for support teams to understand and resolve problems.
3. Higher Conversion Rates:
- Actionable Messages: Interactive elements within RCS messages encourage customers to take immediate action, leading to higher conversion rates for marketing campaigns and promotions.
- Personalization: RCS enables businesses to personalize messages with dynamic content, enhancing the relevance and effectiveness of their communication.
4. Cost Efficiency:
- Unified Platform: RCS provides a single, unified messaging platform, reducing the need for multiple messaging apps and services.
- Scalability: Businesses can scale their messaging campaigns more efficiently, reaching a larger audience with rich and interactive content.
The Future of RCS and Messaging
The future of messaging is undoubtedly exciting, with RCS playing a central role. As more carriers and device manufacturers adopt RCS, we can expect further innovations and improvements in mobile communication.
Upcoming Trends and Innovations:
- AI and Chatbots: Integrating AI and chatbots with RCS will enable businesses to automate customer interactions, providing instant responses and personalized experiences.
- Enhanced Security: As RCS adoption grows, we can expect improvements in security features, including end-to-end encryption, ensuring privacy and data protection.
- Integration with IoT: RCS will likely integrate with Internet of Things (IoT) devices, enabling seamless communication and control of smart devices through rich messaging.
- Expanded Use Cases: Beyond traditional messaging, RCS will find applications in various industries, including healthcare, finance, and logistics, providing enhanced communication and service delivery.
Additional Sections for Comprehensive Coverage
To understand the significance of RCS, it’s important to look back at the history of SMS. The first SMS message was sent in 1992, which simply read, “Merry Christmas.” Over the years, SMS has become ubiquitous, allowing people to send text messages up to 160 characters. However, the limitations of SMS became apparent with the rise of smartphones and multimedia-rich communication needs.
Technical Aspects of RCS
RCS is built on the IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) architecture, which allows it to leverage internet protocols for enhanced communication. This section can delve deeper into RCS’s technical details, explaining how it uses Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) to initiate, maintain, and terminate real-time sessions and ensure compatibility and interoperability across different networks and devices.
Comparison of RCS with Other Messaging Protocols
A detailed comparison of RCS with other popular messaging protocols such as SMS, MMS, and OTT apps like WhatsApp and iMessage can provide readers with a clearer understanding of its advantages. This section can include tables and charts to visually represent the differences in features, security, and user experience.
Case Studies of Businesses Using RCS
Including real-world examples of businesses successfully implementing RCS can provide practical insights. Case studies can highlight how different industries leverage RCS to improve customer engagement, streamline operations, and boost sales. For example, a case study on a retail brand using RCS for personalized marketing campaigns or a healthcare provider using RCS for appointment reminders and patient communication.
Challenges and Limitations of RCS
No technology is without its challenges. This section can explore RCS’s current limitations, such as the need for carrier support, potential security vulnerabilities, and the slow adoption rate in certain regions. It can also discuss ongoing efforts to address these challenges and improve the RCS ecosystem.
User Guides and Best Practices for RCS
Practical guides on how users can set up and maximize RCS on their devices can be very helpful. This section can include step-by-step instructions for Android and iPhone users, tips for troubleshooting common issues, and best practices for ensuring a secure and efficient messaging experience.
Future Outlook and Predictions
A forward-looking section can speculate on how RCS will continue to evolve. This can include expert opinions, predictions for upcoming features, and how emerging technologies like 5G and AI will further enhance RCS capabilities. It can also explore how RCS might impact other communication platforms and what new innovations we can expect in the messaging world.
Historical Context of SMS and the Evolution of RCS
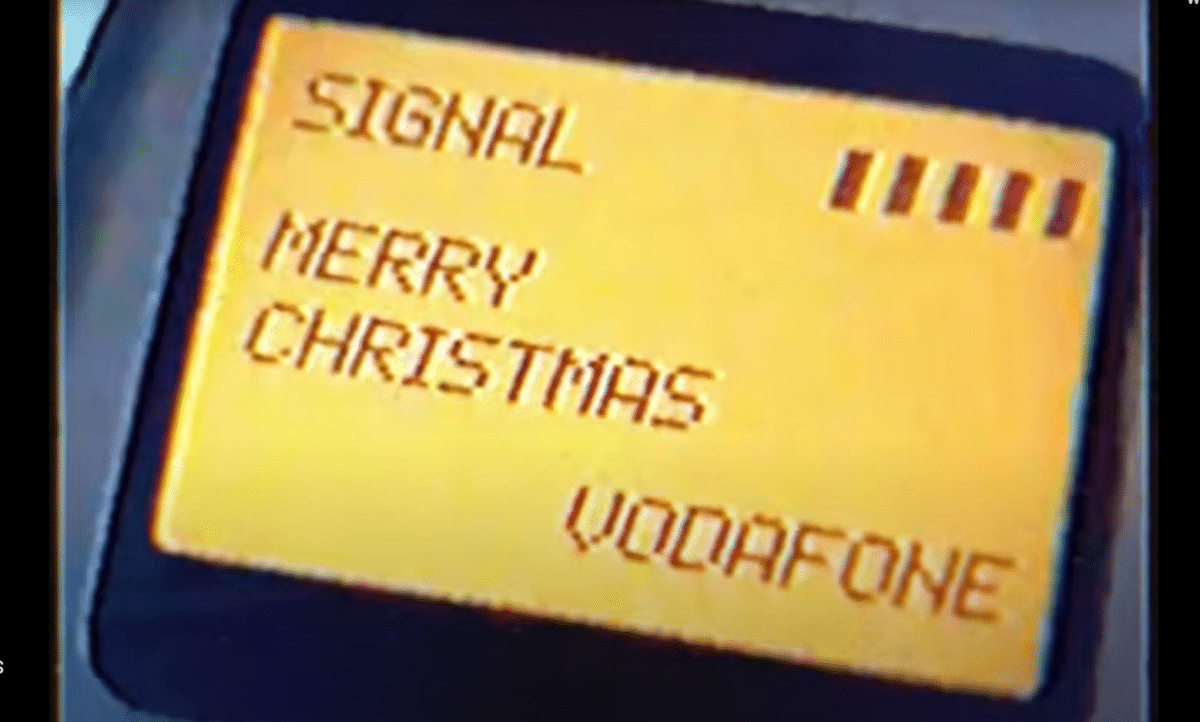
To fully appreciate the significance of RCS, we must look back at the evolution of SMS. SMS, or Short Message Service, has been a fundamental part of mobile communication since its inception. The first SMS message was sent in December 1992 from a computer to a mobile phone on the Vodafone network, reading “Merry Christmas.” This modest beginning marked the start of a communication revolution.
The Rise of SMS
Throughout the 1990s and early 2000s, SMS grew in popularity. It offered a quick, convenient way to send short messages without making a phone call. As mobile phones became more prevalent, SMS usage soared. By 2010, billions of text messages were being sent daily worldwide. Despite its widespread adoption, SMS had several limitations:
- Character Limit: SMS messages were limited to 160 characters, restricting the information conveyed.
- No Multimedia: Standard SMS could not include images, videos, or multimedia content.
- Lack of Interactivity: SMS did not support features like read receipts, typing indicators, or group chats.
The Advent of MMS
Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS) was introduced to address some of these limitations. MMS allowed users to send messages that included multimedia content such as images, audio, and video. However, MMS never achieved the same level of popularity as SMS due to higher costs, slower delivery times, and inconsistent support across devices and carriers.
The Birth of RCS
The limitations of SMS and MMS, combined with the growing popularity of internet-based messaging apps like WhatsApp and iMessage, highlighted the need for a more advanced messaging protocol. In 2008, the GSM Association (GSMA) began developing RCS to enhance the capabilities of traditional SMS and MMS.
RCS aimed to combine SMS’s reliability and universality with the rich features of internet-based messaging apps. The goal was to create a unified messaging standard that could work across all devices and networks, providing a seamless and feature-rich communication experience.
Technical Aspects of RCS
RCS is built on the IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) architecture, a framework for delivering IP-based multimedia services. This architecture allows RCS to leverage internet protocols to provide enhanced communication features.
Key Technical Components:
- Session Initiation Protocol (SIP): RCS uses SIP to initiate, maintain, and terminate real-time sessions. SIP is a signaling protocol widely used for managing multimedia communication sessions such as voice and video calls.
- Presence and Availability: RCS includes presence and availability features, allowing users to see their contacts’ status (e.g., online, offline, busy).
- File Transfer: RCS supports transferring files of various types and sizes, enabling users to share documents, images, videos, and more.
- Interoperability: One key goal of RCS is to ensure interoperability across different networks and devices. The Universal Profile, developed by the GSMA, sets standards for RCS implementation, ensuring consistent functionality regardless of the carrier or device manufacturer.
Comparison of RCS with Other Messaging Protocols
Understanding RCS’s advantages and comparing it with other messaging protocols, such as SMS, MMS, and OTT apps (e.g., WhatsApp and iMessage) is useful.
RCS vs. SMS:
- Features: RCS offers a range of features not available with SMS, including rich media sharing, typing indicators, read receipts, and group chats.
- Interactivity: RCS supports interactive elements like buttons, enabling users to act directly within the message.
- Character Limit: Unlike SMS, RCS has no strict character limit, allowing longer messages.
RCS vs. MMS:
- Quality: RCS allows for higher-quality media sharing than MMS, which often compresses images and videos.
- Cost: RCS messages are typically sent over data networks, potentially reducing costs compared to MMS, which is often more expensive due to higher carrier charges.
OTT Apps vs. RCS:
- Universal Availability: Unlike OTT apps, which require users to install the same app, RCS is designed to work natively across different devices and carriers.
- Integration: RCS is integrated into the default messaging app on many devices, providing a seamless experience without additional apps.

Case Studies of Businesses Using RCS
Real-world examples can illustrate the practical benefits of RCS for businesses. A few case studies highlight how industries leverage RCS to enhance communication and engagement.
Retail Industry
A major retail brand implemented RCS for its marketing campaigns. Using RCS, they could send rich media messages featuring high-quality images and videos of new products. Interactive buttons let customers view more details, purchase, or find the nearest store directly within the message.
Results:
- Increased Engagement: The interactive and visually appealing messages led to higher engagement rates than traditional SMS campaigns.
- Higher Conversion Rates: Customers could immediately act, increasing conversion rates and sales.
Healthcare Industry
A healthcare provider adopted RCS to improve patient communication. They used RCS to send appointment reminders, health tips, and follow-up messages. Patients could confirm or reschedule appointments directly within the message, reducing no-show rates.
Results:
- Improved Patient Compliance: Timely and interactive reminders helped enhance patient compliance with appointments and treatment plans.
- Enhanced Patient Experience: Interacting with messages and accessing information easily enhanced the patient experience.
Financial Services
A financial services company used RCS to enhance customer support and transactional communication. Customers could receive account updates, transaction alerts, and support notifications via RCS. Interactive elements allowed customers to report issues, request assistance, or view detailed account information.
Results:
- Better Customer Support: RCS’s interactive and real-time nature improved customer support efficiency and satisfaction.
- Secure Communication: Enhanced security features provided peace of mind for customers, knowing their financial information was protected.
Challenges and Limitations of RCS
Despite its many advantages, RCS faces several challenges and limitations that must be addressed to achieve widespread adoption.
Carrier Support
RCS requires carrier support to function. While many major carriers have adopted RCS, it is not yet available in some regions and networks. This lack of universal carrier support can hinder the seamless experience that RCS aims to provide.
Device Compatibility
For RCS to work effectively, the sender and recipient must have RCS-enabled devices. While many modern smartphones support RCS, older devices may not be compatible, limiting the reach of RCS messages.
Security Concerns
While RCS offers better security features than SMS, it is still less secure than some OTT apps that provide end-to-end encryption by default. Efforts are ongoing to enhance RCS security, but this remains a concern for users and businesses handling sensitive information.
Adoption Rate
The adoption rate of RCS has been slower than anticipated, partly due to the need for carrier and device support. Additionally, users already accustomed to OTT apps like WhatsApp and iMessage may hesitate to switch to a new messaging protocol.
User Guides and Best Practices for RCS
To help users make the most of RCS, here are some practical guides and best practices for setting up and using RCS on different devices.
Setting Up RCS on Android
- Update Your Messaging App: Ensure you have the latest version of the default messaging app (e.g., Google Messages).
- Enable RCS: Open the messaging app, go to settings, and look for “Chat features” or “RCS” settings. Enable these features.
- Verify Phone Number: You may need to verify your phone number to activate RCS. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete this process.
- Check Carrier Support: Ensure your carrier supports RCS. If not, consider using an RCS-compatible app or contacting your carrier for more information.
Setting Up RCS on iPhone
- Update iOS: Ensure your iPhone is running the latest version of iOS.
- Carrier Settings: Check if your carrier supports RCS and ensure you have the latest carrier settings installed.
- Messaging App: Some carriers may require you to use a specific messaging app that supports RCS. Install and configure the appropriate app if needed.
- Enable RCS: Open the messaging app settings and enable RCS or Chat features if available.
Best Practices for Using RCS
- Optimize Media Quality: RCS can send high-quality media. Ensure your images and videos are clear and relevant to your message.
- Leverage Interactive Features: Use interactive buttons and features to make your messages more engaging and actionable.
- Ensure Compatibility: When sending important messages, verify that the recipient’s device supports RCS to ensure they receive the full experience.
- Monitor Security: Stay informed about the latest security updates and best practices to protect your information and communications.
Future Outlook and Predictions
As RCS continues to evolve, its potential applications and impact on mobile communication are vast and varied. Here are some predictions and trends for the future of RCS:
AI and Chatbot Integration
The integration of AI and chatbots with RCS will revolutionize customer interactions. Businesses can automate responses, provide instant support, and deliver personalized experiences based on customer behavior and preferences. AI-powered chatbots can handle routine queries, leaving human agents to focus on more complex issues.
Enhanced Security Features
As adoption grows, we can expect significant improvements in RCS security. This includes end-to-end encryption for all messages, making RCS a more secure option for sensitive communications. Enhanced security protocols will help build trust among users and businesses.
Integration with IoT
RCS will likely integrate with Internet of Things (IoT) devices, allowing users to control and communicate with their smart devices through rich messaging. For example, users could receive real-time updates and alerts from their smart home systems or control IoT devices directly through RCS messages.
Expanded Use Cases
Beyond traditional messaging, RCS will find applications in various industries:
- Healthcare: Telemedicine, appointment reminders, and patient communication.
- Finance: Secure transactional messages, account updates, and customer support.
- Logistics: Real-time tracking updates, delivery notifications, and customer communication.
- Retail: Personalized marketing campaigns, product launches, and customer engagement.
Global Adoption and Standardization
As more carriers and device manufacturers adopt RCS, it will become a global standard for mobile communication. Efforts to ensure universal compatibility and interoperability will continue, making RCS a reliable and consistent messaging protocol worldwide.
Final Thought!
In conclusion, RCS represents a significant leap forward in mobile communication, transforming how we send and receive text messages. Its introduction to iPhones is particularly noteworthy, as it brings a new level of functionality and interactivity to a wider audience. As RCS continues to gain traction, it promises to unify the messaging experience across all major platforms, making communication more efficient, engaging, and secure.
Providers like YepText are at the forefront of this revolution, offering innovative solutions that help businesses harness the power of RCS. By enabling richer interactions and more personalized communication, RCS is set to become the new standard in messaging.
As we look to the future, the potential applications of RCS are vast and varied. The possibilities are endless, from enhancing customer service and marketing campaigns to integrating with IoT devices and leveraging AI. The evolution of RCS is just beginning, and its impact on the world of communication will undoubtedly be profound and far-reaching.